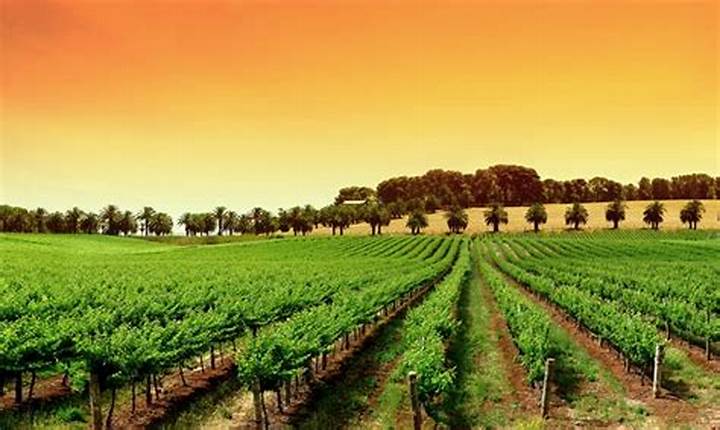
In the enchanting Mediterranean region, a treasure trove of agricultural secrets awaits to be uncovered. From the rolling olive groves of Greece to the sun-drenched vineyards of Spain, this bountiful land has nurtured a rich tradition of sustainable farming practices for centuries. In our quest to understand the harmonious relationship between humans and the earth, we delve into the secrets of Mediterranean agriculture and discover a sustainable path to abundance.
Contents
Principles of Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture is a holistic approach to farming that aims to meet the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. At the heart of Mediterranean agriculture lies a set of principles that guide farmers in their quest for sustainability.
One key principle is the use of organic farming methods. Mediterranean farmers understand the importance of working with nature rather than against it. They avoid the use of synthetic chemicals and instead rely on natural fertilizers, such as compost and animal manure, to enrich the soil. This not only improves soil health but also prevents the pollution of waterways and protects the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
Another principle is crop rotation, a practice that involves growing different crops in a specific sequence on the same piece of land. This helps to prevent the buildup of pests and diseases, as different crops have different nutrient requirements and attract different pests. By rotating crops, Mediterranean farmers are able to maintain soil fertility, reduce the need for chemical inputs, and increase overall crop yields.
Intercropping is yet another important practice in Mediterranean agriculture definition. This involves planting different crops together in the same field, allowing them to complement and support each other’s growth. For example, legumes like peas and beans can be intercropped with cereal crops like wheat or barley. The legumes fix nitrogen in the soil, benefiting the cereals, while the cereals provide a natural trellis for the legumes to climb. This symbiotic relationship enhances soil fertility, reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers, and increases overall productivity.
Advantages of Mediterranean Agriculture
Mediterranean agriculture offers numerous advantages that make it a sustainable and efficient farming system. One of the key advantages is the region’s favorable climate. With its long, hot summers and mild winters, the Mediterranean provides the ideal conditions for a wide range of crops to thrive. This allows farmers to grow a diverse array of fruits, vegetables, grains, and herbs, ensuring a year-round supply of fresh and nutritious produce.
Another advantage is the abundance of sunlight in the Mediterranean region. The ample sunshine provides the energy needed for photosynthesis, allowing plants to grow and produce food efficiently. This natural resource is harnessed by Mediterranean farmers to cultivate crops that are rich in flavor and nutrients.
Furthermore, the Mediterranean’s proximity to the sea offers access to a valuable source of water. While water scarcity is a global concern, Mediterranean agriculture benefits from the sea’s proximity, allowing for the development of innovative irrigation systems. From ancient terraced vineyards to modern drip irrigation techniques, Mediterranean farmers have mastered the art of water management, ensuring that crops receive adequate hydration while minimizing water wastage.
Traditional Mediterranean Crops and Farming Practices
The Mediterranean region is renowned for its unique and diverse range of crops. Olive trees, with their silver-green leaves and golden fruits, are synonymous with the Mediterranean landscape. Olive cultivation has been practiced for thousands of years, and the region is now the largest producer of olive oil in the world. The trees are well adapted to the Mediterranean climate and require minimal inputs, making them a sustainable and profitable crop for farmers.
Grapes are another iconic crop of the Mediterranean. The region’s warm climate and fertile soils provide ideal conditions for viticulture. From the rolling hills of Tuscany in Italy to the sun-kissed plains of Andalusia in Spain, vineyards have thrived for centuries, producing some of the world’s finest wines. Mediterranean farmers have perfected the art of grape cultivation, implementing techniques such as terracing, which prevents soil erosion and optimizes water usage.
In addition to olives and grapes, Mediterranean farmers cultivate a wide range of other crops. Citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits thrive in the region’s mild winters and hot summers. Tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, and zucchinis add vibrant colors and flavors to Mediterranean cuisine. Grains like wheat, barley, and rice are staple crops that have sustained communities for generations.
Impact of Mediterranean Agriculture on the Environment
Mediterranean agriculture has a minimal environmental impact compared to conventional farming practices. By embracing organic methods and minimizing the use of synthetic inputs, Mediterranean farmers protect the soil from degradation and ensure its long-term fertility. This not only benefits their own crops but also preserves the biodiversity of the surrounding ecosystem.
The use of crop rotation and intercropping reduces the need for chemical pesticides and fertilizers, thus minimizing the release of harmful substances into the environment. By relying on natural pest control methods, such as attracting beneficial insects or using physical barriers, Mediterranean farmers maintain a balance between pests and their natural predators. This reduces the risk of pest outbreaks and the need for chemical interventions, resulting in a healthier and more sustainable farming system.
Furthermore, the traditional farming practices of the Mediterranean, such as terracing and drip irrigation, help to conserve water and prevent soil erosion. Terracing involves creating level platforms on sloping land, which reduces the speed of water runoff and allows it to infiltrate into the soil. This prevents erosion and helps to retain moisture, making the land more resilient to droughts and floods. Drip irrigation, on the other hand, delivers water directly to the roots of plants, minimizing evaporation and ensuring efficient water usage.
Innovations in Mediterranean Agriculture
While traditional farming methods have served Mediterranean farmers well for centuries, they have also embraced innovation to further enhance their productivity and sustainability. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in agroecology, a field that combines ecological principles with agricultural practices.
Agroecology promotes the use of ecological processes and biodiversity to optimize crop production. It emphasizes the importance of crop diversity, encouraging farmers to grow a variety of crops in order to enhance soil health and reduce pest pressures. By adopting agroecological practices, Mediterranean farmers are able to create resilient and productive farming systems that are less reliant on external inputs.
Technological advancements have also played a role in improving Mediterranean agriculture. For example, precision agriculture utilizes sensors, satellite imagery, and data analytics to monitor crop health and optimize resource allocation. This allows farmers to apply inputs such as water and fertilizers only where and when they are needed, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
Benefits of Sustainable Mediterranean Agriculture
Sustainable Mediterranean agriculture offers numerous benefits, both for farmers and the broader society. By embracing organic farming practices and minimizing synthetic inputs, farmers are able to produce high-quality crops that are free from harmful residues. This benefits consumers, who can enjoy nutritious and flavorful produce while minimizing their exposure to chemicals.
Sustainable agriculture also contributes to the preservation of rural communities and cultural heritage. By supporting small-scale farmers and encouraging traditional farming practices, Mediterranean agriculture helps to maintain vibrant rural economies and preserve the unique landscapes and traditions of the region. This not only enhances the quality of life for farmers but also provides opportunities for agritourism, which attracts visitors from around the world and helps to diversify local economies.
Furthermore, sustainable agriculture has a positive impact on climate change mitigation and adaptation. By sequestering carbon in the soil through practices like composting and cover cropping, Mediterranean farmers contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. The use of efficient irrigation techniques and water management strategies also helps to conserve water resources, which are increasingly under pressure due to climate change.
Mediterranean agriculture holds the key to a sustainable path to abundance. By embracing organic farming principles, crop rotation, and intercropping, Mediterranean farmers have managed to achieve impressive yields while safeguarding the delicate ecosystem. With its diverse range of crops, favorable climate, and innovative farming practices, the Mediterranean region serves as a shining example of how agriculture can coexist harmoniously with nature. Let us learn from the secrets of Mediterranean agriculture and embark on a journey towards a more sustainable future.